Theme: Towards a world free from the threat of Infectious diseases
Infectious Diseases Conf 2019
Infectious Diseases, Prevention and Control scheduled on March 21-22, 2019, in Dubai, will give useful proof based methodologies to connect with the workforce and reduce the spread of intense healthcare-associated infections. Infectious Diseases Conf 2019 is to promote the health awareness which incorporates keynote meetings, symposiums, roundtable discussions, abstracts, poster presentations and workshops on Infection Prevention and Control, associated with infectious diseases. The objective is to bring together a multidisciplinary gathering to identify important issues relating to Infection Prevention and Control in Russia, Asia Pacific, the United States, Europe over the world. Particularly the boundaries to a wider recognition of the disease, and to develop a coordinated action plan.
Infectious Diseases, Prevention and Control is an international platform for presenting research about Infectious Diseases, control and Therapy. Infectious Diseases are disorders caused by organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Infectious diseases may be of waterborne, foodborne, vector-borne, airborne in human beings as well as in plants and animals. Infectious diseases basically emphasize on the pathogenesis of the bacteria and their therapeutic measures, coalesce of branches of microbiology especially clinical and diagnostic microbiology which deals with the cure and prevention of the Infectious Diseases. It represents an increasingly important cause of human morbidity and mortality throughout the world. Vaccine development is thus of great importance in terms of global health. The conference also welcomes International exhibitions from corporate sectors to showcase the recent advancements in Infections and its Therapy.
Importance and Scope:
Infectious diseases are also known as communicable Diseases, and the subject of dealing with Infectious diseases is called infectiology, which deals with the diagnosis, control and treatment of infections. An infectious disease (ID) specialist's practice may consist largely of managing nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections, or it may be out-patient based. ID specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immunodeficiency. The market report organizes information from diverse sources into a cohesive unit that includes an overview, global implications of infectious diseases, infectious diseases by type, treatment and prevention, emerging pharmaceutical and diagnostic products and an applicable patents section. Information is organized by type of infectious disease (i.e., bacterial, viral, parasitic) and appropriate treatments, both current and anticipated.
In the new bio-economy, Infectious diseases play a very important role in representing major global challenges, upgrading waste streams to valuable food ingredients, counteracting life-style diseases and antibiotic resistance through the gut biota, making crop plants more resistance to extreme climatic change conditions, and functioning as host for the production of new biological drugs for treatments of diseases.
Why it’s in Dubai, UAE:
Dubai is the second largest emirate by its territorial size after the capital of Abu Dhabi and is the most populous city and emirate in the UAE. Dubai is located on the southeast coast of the Persian Gulf and it is one of the seven emirates that put together up the country. The city heads up to the Dubai-Sharjah-Ajman metropolitan territory. Dubai will host the World Expo 2020. Today, Dubai has emerged as a cosmopolitan city that has grown progressively into a worldwide city and a business and social centre of the Middle East and the Persian Gulf. Starting in 2012, Dubai is the most extravagant city in the Middle East. In 2016, Dubai’s inn rooms were evaluated as the second most lavish on the planet, after Geneva. In 2014, Dubai and the UAE overall was positioned first in the Middle East as far as Women's rights.
Why to Attend?
Infection Diseases, Prevention and Control 2019 is giving a worldwide stage to analysts that afford new insights into the concealed methods of Infection Control. World-eminent speakers, guest of honours, and the most up to date upgrades are particular components of this gathering and with individuals from around the globe concentrated on finding out about uncommon illnesses and its advances; An expanding number of distinguished methods makes it important to complete propelled research here of irresistible sicknesses. Infection Prevention 2018 is your best chance to achieve the biggest collection of members, conduct presentations, disseminate data, B2B meetings, meet with potential scientists, trade learning on late improvements and make an unmistakable imprint by invigorating development at this event.
Target Audience
Microbiologists
Bacteriologists
Virologists
Parasitologists
Mycologists
Pathologists
Pharmacists
Epidemiologists
Dermatologists
Neurologist
Ophthalmologist
Cardiologist
Health Care Professionals
Academic Professionals
Medical & Pharmacy Companies
Students
Researchers
Research Associates
Major Infectious Diseases Research Centre Middle East:
Qatar Biomedical Research Institute
Molecular Biology and Genetics Lab
Freiburg Medical Laboratory
The Center for Infectious Diseases Research (CIDR)
Major University doing Researches on Infectious Diseases in UAE:
University of Sharjah
United Arab Emirates University
Abu Dhabi University
Ajman University
Top Universities Worldwide:
UCL Institute of Epidemiology and Healthcare
University of Sheffield
Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society
Columbia University
University of Maryland
Swedish Institute for Infectious Disease Control
Uppsala University
University of Gothenburg
University of Otago
Oslo University
University of Pittsburgh
Emory Health Sciences
Queensland University of Technology
University of Liverpool
University of Colorado Denver
Infectious Diseases Society of America
Medical College of Georgia at Georgia Regents University
Major Infectious Disease Societies around the Globe:
European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
International Union of Microbiological Societies
Federation of Infection Societies
Canadian Society of Microbiologists
British Infection Association
Federation of European Microbiological Societies
Welsh Microbiology Association
Clinical Virology Network
American Society for Microbiology
Society for General Microbiology
Track 1: Infectious Diseases and Vaccines
Infectious diseases also known as contagious diseases are diseases caused by pathogenic organisms, such as viruses, microscopic organisms, bacteria or parasites. Numerous organisms live in and on our bodies. They’re mostly harmless or but in some cases are helpful, yet under specific conditions may cause the disease. Some infectious diseases can be spread from infected individual to a healthy individual. When exposed to an infected animal, humans that possess a pathogenic organism also becomes infected. The record of human suffering and death caused by smallpox, cholera, typhus, dysentery, malaria, etc. establishes the calibre of infectious diseases. Microorganisms are tiny living things that are found everywhere - in air, soil and water. Microorganisms that cause disease are together called pathogens. Infectious diseases vaccines are the vaccines which prevent the infectious diseases like Haemophilus influenza, Diphtheria, hepatitis b, measles, meningitis, serotype b infection, tetanus, rubella, tuberculosis, yellow fever are preventable through immunizations. An infectious disease for which an effective preventive vaccine exists is called vaccine-preventable disease. If a person procures a vaccine-preventable disease and if he dies from it then the death is considered a vaccine-preventable death.
Track 2: Mechanism of Resistance
Mechanism of resistance is because of the inactivation or change in the target site of the antibiotic that decreases its binding capacity, to avoid the antibiotic effect and the diminished intracellular anti-microbial gathering, decreasing permeability and/ or increasing active efflux of the antibiotic. A host can evolve two kinds of defence mechanisms to increase its wellness when tested with a pathogen- resistance and tolerance. It is essential to differentiate between these two defences mechanisms since they have diverse epidemiological and pathological impacts. Expanded comprehension of these defences could lead to more effective treatment methods and a better description of host-parasite interactions.
Track 3: Drug Interaction in Infectious Diseases
Drug interactions in infectious diseases are a major source of medical harm that can be prevented. It is notable that drug interactions represent a major risk to patients. Even a casual look at approved drug product labels for anti-infective drugs, such as azole antifungal drugs, direct-acting antivirals for HCV, HIV drugs and anti-mycobacterial agents unveil that drug interactions present a huge challenge for patients and their healthcare providers. Concerns regarding the interaction of drugs rise as the knowledge of pharmacology advances. The interactions may be due to non-CYP enzymes, CYP enzymes, and changes in gastric pH, the ever-growing list of drug transporters and more. Other considerations incorporate interactions due to herbal medications, food components and biological products.
Track 4: Immunology of Infection
Immunology is a branch of biology that covers the investigation of insusceptible systems in all life forms. Regardless of whether an infectious disease is an “old associate’’ or another developing risk, the immune system’s battle against it is generally the first line of defence it experiences The immune system has built up a number of ways to deal with controlling viral and bacterial disease which range from direct killing of pathogen to complex cytokines that hinder replication. Pathogens have countered by building up an assortment of immune evasion mechanisms that repress cytokine work and prevent resistant acknowledgement of tainted cells. With vaccines and effective medications, the immune system’s attempt to destroy the infectious agents or infected cells are every now and again the main intends to battle.
Track 5: Bacterial Infections
A bacterial infection is a rapid growth of a harmful strain of bacteria on or inside the body. Harmful bacteria can cause a few illnesses like pneumonia, meningitis, and food poisoning. Bacterial infections are one of the main causes of foodborne illness. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, fever, chills, fatigue and abdominal pain. Most of the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are caused by harmful bacteria. Most of the times they are not related to any symptoms of the disease but still can cause significant damage to the reproductive system. Bacterial skin infections are generally caused by gram-positive strains of bacteria such as Streptococcus and Staphylococcus. Some of the bacterial infections include boils, impetigo, and folliculitis.
Track 6: Viral Infections
Viruses are like hijackers. They attack typical living cells and use them to multiply and produce other viruses like themselves. This can slaughter, damage, or change the cells and make sick. Different viruses attack certain cells in the body such as the liver, respiratory system, or blood. Viruses are made of genetic material inside of a protein coating. Viruses cause common infectious diseases like common cold, flu and warts. Viruses also cause serious illnesses like HIV, Ebola and smallpox. Vaccines can help in preventing many viral diseases.
Track 7: Fungal Infections
Fungal Infectious diseases are often caused by fungi that are familiar with the environment. Some types can be harmful to health but most types are not dangerous. Mild skin diseases caused by fungi can look like a rash and are very common. Fungal diseases in the lungs are like other illnesses such as tuberculosis or flu. Fungal infections are very common in humans and are normally not very serious if they are treated quickly and correctly.
Track 8: Foodborne and Waterborne Infections
Foodborne infections, ordinarily called food poisoning/nourishment harming, and waterborne infections are conditions caused by eating or drinking food or water that is contaminated by microbes or the toxins produced by the organisms. They commonly cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhoea, nausea and abdominal pain. There are numerous non-infectious causes of illness from contaminated food and water and a few microbes results in infections other than in the digestive tract. Food and water-borne infectious diseases are considered to be the most common of all acute illnesses. It occurs worldwide, and the incidence varies from country to country. In recent years, detection of outbreaks of viral origin, particularly noroviruses, has been increasing worldwide. Two or more related cases of suspected food or water-borne illness must be reported within 24 hours of diagnosis (presumed or confirmed).
Track 9: Respiratory and Blood Stream Infections/Bacteraemia/Blood Poisoning
Bloodstream infection (BSI) is possibly a life-threatening condition with a case mortality rate of 30-40%. Bloodstream infections/ blood poisoning occurs when a bacterial infection somewhere in the body such as in the lungs or skin which enters the circulation system. This is threatening because the bacteria and their toxins can be brought to the circulation system of the body to the entire body. BSI can be categorized as hospital-acquired (HA), or community-acquired (CA) depending on the site of receiving infection and hazard factors. Infectious diseases are caused by germs- bacteria, viruses, microscopic organisms or other pathogenic microorganisms. Germs that can infect the respiratory framework can ordinarily be spread through saliva and mucus (also known as "respiratory secretions") removed when a man talks, coughs, laughs or sneezes. A portion of these germs spreads through small droplets to stay suspended in the air and travel over long distances. Another person may fall ill when he inhales the aerosols containing infectious microbes or when the microbes contact their mucous membranes.
Track 10: Dental and Oral Infectious Diseases and Control
Oral infections are one of the most common diseases in humans. The two most common oral infections are periodontal disease and caries ailment. Dental caries is the most well-known chronic disease of adolescence and is greatly neglected among youngsters. Periodontal illness is the most widely recognized infectious disease of adults. At least 1/3 of the population is affected by chronic periodontitis, a bacterially instigated destruction of the attachment of the tooth to the bone. Non-disposable things like dental tools should be cleaned and disinfected between patients. Disposable dental instruments and needles are never reused on another patient. Contamination control precautionary measures conjointly required for all dental staff associated with quiet care to utilize defensive clothing, for example, gloves, covers, outfits and eyewear. FDI recommends that every oral professional should be familiar with post-presentation activity for the administration of occupational exposures to blood-borne pathogens, and proprietors of oral human services centres should organize arrangements inside the workplace to guarantee proper and sparing administration of such episodes.
Track 11: Dermatological Infectious Diseases and Control
Dermatology diseases include frequent skin rashes to acute skin infections, which is caused due to allergens, system disorders, infections, medication and heat. One of the most common skin disorders is dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis is relating current (chronic) condition that causes inflamed skin and anxiousness. Patients with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), are at high risk of developing a variety of skin diseases and problems because of their compromised immune system. HIV-related skin disorders may develop or appear from fungal, bacterial or viral skin conditions, skin allergies, skin cancer or malignancies or from harmful drug interactions. At an absolute minimum, the earth should be perfect and sterile with proper surfaces. Hand washing should be accessible. Sterile pion of such episodes.
Track 12: Nosocomial or Hospital Acquired Infection and Control
Nosocomial infection is also known as Hospital-acquired infection (HAI) is an infection that is acquired in a health care facility or in a hospital. Such an infection can be acquired in a nursing home, in a hospital, outpatient clinic, rehabilitation facility or other clinical settings. Infection is spread to the vulnerable patient by various means in a clinical setting. Medical services staff can spread the disease in addition to the equipment that is contaminated, air droplets of the infectious person or bed linens. Measures of infection control incorporate distinguishing patients at risk of nosocomial infections, following standard precautions to decrease transmission and systems to reduce CR0BSI, VAP and environmental factors and engineering spread out additionally should be accentuated upon.
Track 13: Pediatric/Childhood Infectious Disease
Pediatric infectious diseases also known as childhood infectious diseases are the infectious diseases which are caused in children of various age groups. Pediatric infectious diseases experts deal with the infections occurring in children and the treatment method fluctuates from children to adults. Common pediatric infections include Pneumonia- diagnosed in nearly 2% of infants < 1 year and in 4% of children aged 1 to 5 years. It is estimated that 90% of pediatric pneumonia are caused by viral agents. Other infections also include Otitis Media which is caused in children who live with the adults who smoke.
Track 14: Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Control
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) are infectious diseases that pass from the infected individual to the healthy individual through sexual contact. Sexually transmitted diseases are also known as Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) or Venereal Diseases (VD). In some case,s STDs can spread by using the unsterilized drug needles, from mother during the birth of the child and breastfeeding, and transfusion of blood. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates there are more than 1 million cases of STDs acquired globally each day. STI control is a general health outcome estimated by reduced incidence and commonness. The way to accomplish this include: (i) promoting and providing condoms and other means of prevention; (ii) an empowering domain; and (iii) dependable information.
Track 15: Plant Infectious Diseases
Plants developing infectious diseases include organisms such as viruses, virus-like organisms, piroplasms, oomycetes, fungi parasitic plants and nematodes. Common pathogenic infection methods are toxins, cell wall degrading enzymes, cell wall degrading enzymes. There are various cases of obliterating plant disease impacts such as chestnut blight and Irish potato starvation, as well as recurrent severe plant diseases like citrus canker, rice blast and soybean cyst nematode.
Track 16: Veterinary/Animal Infectious Disease
Infectious diseases of livestock are globally a major threat to animal health and welfare and their proper control is important for agronomic health, for protecting and national and international food supplies and for mitigating rural poverty in developing countries. Animal diseases constitute an important threat to human health since the rise of human diseases is dominated by zoonotic pathogens. Zoonotic contaminants that are transmissible either directly or indirectly between animals and humans are on the expansion or posture noteworthy threats to human health and the present pandemic status of new influenza A (H1N1) is a typical case of the test displayed by zoonotic infections. Veterinary scientists commonly combine with epidemiologists.
Track 17: Ophthalmological Infectious Diseases
A large number of parasites like the viruses, bacteria, and fungi that can invade the human body are also capable of attacking the interior or surface of the eye. The most common eye infection is conjunctivitis which is caused by adenovirus (a type of common cold virus). This infection of the conjunctivitis is sometimes referred to as Pinkeye and is most common in children. There are numerous causes of conjunctivitis and are usually classified as bacterial, viral or fungal.
Track 18: Emerging Infectious Diseases and Recent Outbreaks
Emerging infectious disease (EID) are infections that appear for the first time in a population, or that may have appeared previously. Outbreaks are the occurrence of disease cases in an abundance of what would normally be expected for a community, season or a geographical area (WHO). Ebola haemorrhagic fever (EHF) also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) is caused by four unique strains of Ebola virus; these viruses infect humans and nonhuman primates. Signs and symptoms of Ebola virus disease include a migraine, unexpected fever, joint agony, muscle hurts, sore throat, and weakness. Series of Ebola symptoms include rash, hiccups, stomach pain, internal and external bleeding in many patients, vomiting, and diarrhoea. Ebola infection spreads by contact with blood and discharges that stay on dress, needles and/or syringes or other medical supplies used to treat Ebola-infected patients, direct contact with blood and secretions. Zika virus disease is caused by a virus transmitted basically by Aedes mosquitoes, which bite during the day. Symptoms are generally gentle and include conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, fever, malaise or a headache. Zika virus infection during pregnancy can result in infant to be born with microcephaly and other congenital distortions, known as Zika syndrome. Zika virus infection is also associated with other complexities of pregnancy including miscarriage and preterm birth.
Track 19: Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases
Gene therapy confines considerable potential for the treatment of both infectious diseases and hereditary genetic disorders. Human gene therapy is defined as the presentation of new genetic material into the cells of a person with the purpose of generating a therapeutic advantage for the patient. Gene therapy is being researched as an alternative for a number of infectious diseases that do not agree to the standard clinical administration. Gene therapy for infectious diseases needs the introduction of genes outlined to particularly repress or block the gene expression or function of gene products, to such an extent that the replication of the infectious agent is blocked or constrained. In addition to this intracellular interference, gene therapy may be used to mediate in the spread of the infectious agent at the extracellular level. This could be accomplished by sustained expression in vivo of a discharged inhibitory protein or stimulation of a specific immune response.
Track 20: Infection Prevention and Control Guidelines
Infection Prevention guidelines to educate patients, families, guests and carers about human services related infection, what activities medicinal services offices may have set up to ensure contaminations are counteracted however much as could reasonably be expected, and what they can do to restrain the spread of contaminations. Healthcare providers have a social duty to protect patients and prevent pointless damage. In life-threatening emergencies requiring immediate action, healthcare providers should measure the relative risk to patient life and decide the most proper disease control practice under those circumstances.
Infectious Diseases Diagnostics Market
The market for infectious disease molecular diagnostics tests incorporates reference research centres, hospitals, blood banks. Size is predicted to grow at 9.42% CAGR from 2018 to 2023 and it is determined that the Middle East and Africa market was valued at USD 1.35 billion in 2018 and is depended upon to accomplish USD 2.12 billion by 2023. Diagnostics of the Infectious disease includes a different technique to check for the presence of a foreign antigen/organism with the assistance of numerous diagnostic tools. Conditions of the Infectious disease are highly widespread in underdeveloped regions due to the lack of awareness for individual cleanliness, minimal health care expenditures, and absence of effective physician services. Rising instances of infectious diseases in developed economies are additionally expected to help the market development. This has resulted in vitro diagnostic gadget makers to invest in emerging countries. These organizations are making efforts to develop and popularise cost-effective tools for the diagnosis of infectious diseases.
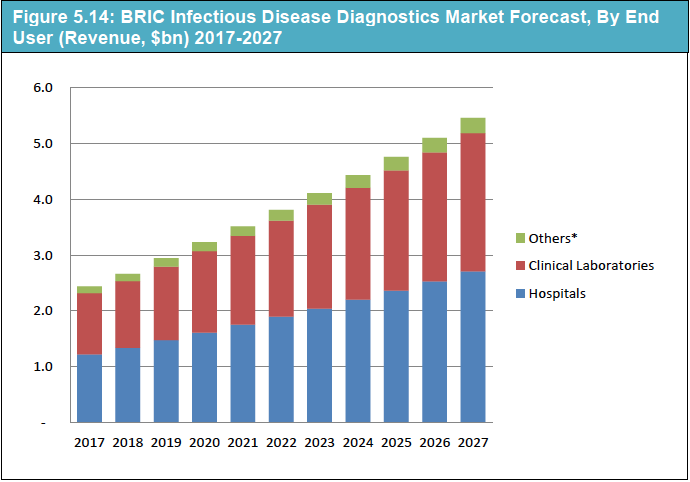
Disease diagnostics are utilized for are utilized for in form of a quick, precise test result. Disease diagnostics are on a rise even if it is time-consuming. The infectious disease epidemics are spreading around the world, thereby increasing the demand for diagnostic tests. Additionally, the occurrence of AIDS, malaria, and other diseases are also on increase, creating a vigorous demand for infectious disease diagnostics. Many government-financed programs all over the globe are progressively providing free screening and tests in order to increase awareness, precisely diagnose diseases, and limit the chances of infection. Such activities are foreseen to help the market development in the following couple of years. However, diagnostic kits are highly priced and manufacturers still have a poor assortment channel for working across emerging economies. These two components are anticipated to be the key difficulties to rapid revenue growth of the global infectious diseases diagnostics market.
Recent Outbreak (Zika virus):
Zika virus is the current outbreak occurring from in many countries. It is affected to people primarily through the bite of an infected Aedes species mosquito (Ae. aegypti and Ae. albopictus). Zika can also be passed through sex from a person who has Zika to his or her sex partners and it can also spread from a pregnant woman to her fetus. The National Institutes of Health, USA say trials for Zika vaccine is about to start in September this year. Depending on the results, larger trials could begin at the start of 2017. Up to date, 2015-16 total 69 Zika Virus cases reported with 16 live born infants with birth defects and 5 total pregnancy losses with birth defects.
Infectious Diseases Therapeutic Market
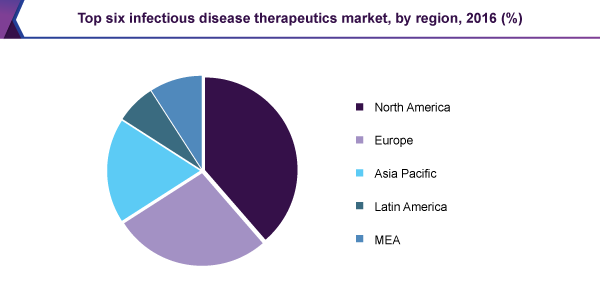
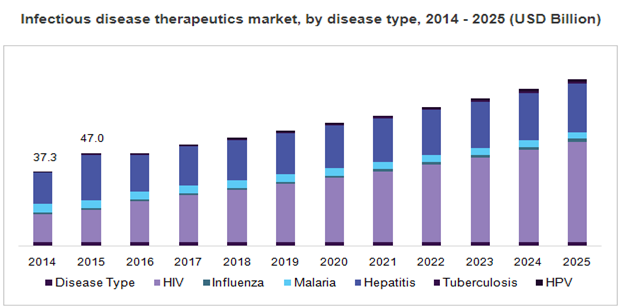
The Middle East and Africa Infectious Disease Therapeutics Market accounts for USD 8.42 Billion in 2018 and assessed to achieve 12.29 USD Billion by the end of 2023 with a developing potential of 7.877 %. The Middle East and Africa Infectious disease therapeutics market are categorized based on Mode of treatment into Drugs and Vaccines. The drugs are further segmented into oral administration, topical, injections and others. Based on the target organism the market is categorized into antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiparasitic and others. Based on infection type the market is categorized into Bacterial, viral, fungal, parasite and others. Based on distribution channels the market is categorized into hospitals, clinics and others. Based on Geography, the Middle East and Africa Infectious disease therapeutics market is analyzed under various regions namely the Middle East and Africa. The global infectious disease therapeutics market size was valued at USD 46.88 billion in 2016 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecast period.
Infection Control 2018
Sensing the raising importance of Infectious Diseases prevention, control, treatment and cure, Conference Series LLC Ltd hosted 3rd International Conference on Infection, Disease Control and Prevention (Infection Control 2018), scheduled from June 25-26, 2018 in Vancouver, Canada with a theme “To Safeguard Public Health”. The conference was successful in gathering eminent speakers from various reputed organizations and their paramount talks enlightened the gathering.
The pragmatic meet organized by Conference Series LLC Ltd received a generous response from the Editorial Board Members of Conference Series LLC Ltd Journals as well as expertise from academia, talented researchers and young student community. Researchers and students who attended from different parts of the world made the conference one of the most successful and productive events in 2018 from Conference Series LLC Ltd. The conference was marked by the presence of renowned Speakers, Young Researchers, Students and Business Delegates driving the three-day event into the path of success with thought-provoking keynote and plenary presentations.
The meeting was carried out through various sessions, in which the discussions were held on the following thought-provoking and celebrating scientific tracks:
- Infection Treatment and Control
- Emerging infectious diseases
- Infection Novel Therapies
- Treatment & Diagnosis
- Healthcare-associated Infection (HAIs)
- HIV/AIDS from STDs & STIs
- Infection by Zoonoses
- Disinfection/Sterilization
- Infections from Plants
- Infections During Pregnancy
- Pediatric Infectious Diseases
- Practices and Awareness
- Multi Pathogen Infections
- Practical Guidelines
- Infection Control Business
Infection Control 2018 Proceedings
- Key Note Forum
- Tracks
- Posters and Accepted Abstracts
The conference was embarked with an opening ceremony followed by Keynote presentations, Workshop and a series of lectures delivered by both Honourable Guests and members of the Keynote forum. The adepts who promulgated the theme with their exquisite talk were:
1. Moderators
- Dr Hana Zelenkova, DOST Svidnik, Slovakia
2. Session Chairs
- Dr Hana Zelenkova, DOST Svidnik, Slovakia
- De Nardo E, GOJO Industries, USA
- KC Santosh, The University of South Dakota, USA
3. Keynote Presentations
- Anil Kaul, Oklahoma State University, USA
- Bienfang Lei, Montana State University, USA
- KC Santosh, The University of South Dakota, USA
- Hana Zelenkova, DOST Svidník, Slovakia
- Sara Dann, The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, USA
Conference Series LLC Ltd offers its heartfelt appreciation to Societies and Organizations, Organizing Committee Members, adepts of the field, various outside experts, company representatives and other eminent personalities who interlaced with Conference Series LLC Ltd in supporting and making the conference a grandiose event.
Your rejoinder is our inspiration, keeping this motto in mind and being witnessed the triumph of Infection Control 2018, Conference Series LLC Ltd is delighted to announce the next event, "14th International Conference on Infectious Diseases, Prevention and Control" to be held during March 21-22, 2019, Dubai, UAE.
Contact us for more queries…!!!!
Conference Highlights
- Immunology of Infection
- Bacterial Infections
- Viral Infections
- Fungal Infections
- Mechanism of Resistance
- Drug Interaction in Infectious Diseases
- Food-borne and Waterborne Infections
- Respiratory and Blood Stream Infections/ Bacteraemia / Blood Poisoning
- Dental and Oral Infectious Diseases and Control
- Dermatological Infectious Diseases and Control
- Ophthalmological Infectious Diseases
- Nosocomial or Hospital Acquired Infection and Control
- Emerging Infectious Diseases and Recent Outbreaks
- Pediatric/ Childhood Infectious Disease
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Control
- Plant Infectious Diseases
- Veterinary/Animal Infectious Disease
- Infection Control in Emergency
- Infection Prevention and Control Guidelines
- Infectious Diseases and Vaccines
- Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | March 21-22, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
- Air & Water Borne Diseases
- Journal of Bacteriology & Parasitology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by