Theme: Theme: “Discovering fresh insights for a disease-free lifeâ€
Renowned Speakers
INFECTIOUS DISEASES CONF 2022
ME Conferences invite attendees from all over the world to attend the "17th World Conference on Infectious Diseases, Prevention and Control" which will be held on November 17-18, 2022. This brings together and promotes keynote addresses, oral presentations, poster presentations, and electronic posters. Theme: "Discovering fresh insights for a disease-free life" is the conference's core subject.
Infectious Diseases Congress 2022 will serve as a platform for Infectious Diseases Specialists, Infectious Diseases Researchers, Scientists, Faculties, Students, Business professionals, Healthcare professionals, clinicians, researchers, academicians, foundation leaders, Infectious Diseases Associations and Societies, direct service providers, policymakers, Medical Colleges, Pharmaceutical Companies and Industries, Medical Devices Manufacturing Companies, Drug Manufacturing Companies, Medical Colleges, Pharmaceutical Companies and Industries, Medical Devices Manufacturing Companies, Drug Manufacturing Companies, Industries and others involved in this area are invited to discuss their key perspectives on monitoring Infectious Diseases-related topics.
Why to attend??
This is the finest opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of individuals from the infectious diseases, with members from all around the world dedicated on learning about Infectious Diseases and its accomplishments. At this two-day event, give presentations, disseminate information, interact with existing and future scientists, create a splash with new medicine advances, and get your name out there. This conference features world-renowned lecturers, cutting-edge techniques, discoveries, and the most recent updates in Infectious Diseases
Target Audience:
- Microbiologists
- Pathologists
- Epidemiologists
- Dermatologists
- Allergists
- Immunologists
- Pediatricians
- Physicians
- Pharmacists
- Neurologists
- Infection Prevention and Infection Control Specialists
- Academic and Health care Professionals
- Research Associates
- Health Care Associations & Societies
- Medical & Pharmacy Companies
- Medical Devices and drug Manufacturing Companies
- Laboratory Technicians and Diagnostic Companies
- Business Entrepreneurs and Industrialists
- Students
Track 1 Infectious Diseases Prevention and Control
Cleaning germs from filthy surfaces without paying attention to appropriate hygiene might transmit them to other locations. While doing our regular duties, we may unintentionally take up germs on our hands. They would then spread to everything we come into touch with until we had a chance to wash our hands again.
Furthermore, when a person has a viral illness such as influenza, the minute drops of moisture from their lips can transmit germs all over the place when they inhale, wheeze, or hack.
- Hand washing
- Asepsis
- Disinfection Methods
- Reduce Number of Sex Partners
- Abstinence
- Early Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
- Standard Environmental Cleaning
- Sterilization Methods
Track 2 Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19)
Coronavirus Illness (COVID-19) is a recently found Corona virus strain that causes an infectious disease. The majority of individuals who get COVID-19 develop mild to moderate symptoms and overcome without any supplementary therapy.
Coronaviruses are a group of closely linked RNA viruses infecting mammals and birds. They cause a variety of illnesses in people and birds, ranging from mild to fatal. Some cases of respiratory illness in humans (which is also caused by various viruses, mostly rhinoviruses) are mild, but SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 are caused by a variety of lethal variations. They induce diarrhea in cows and pigs, as well as hepatitis and inflammation in mice.
Track 3 Medical and Vaccine Research for Covid-19
Medical research (also known as biomedical research) encompasses a wide range of studies, ranging from "basic research" (also known as bench science) involving fundamental scientific principles that may relate to a preclinical understanding to clinical research, which involves studies of people who may be subjects in clinical trials.
The pharmaceutical industry's drug development process includes both clinical and preclinical research phases, with the clinical phase signified by the phrase clinical trial. Only a portion of clinical or preclinical research is focused on a single pharmacological goal. Pharmaceutical research is just a minor component of medical research since it forms the foundation for basic and mechanism-based knowledge, diagnostics, medical devices, and non-pharmaceutical therapy.
Track 4 Infectious Diseases Caused by Bacteria
Bacterial Disease is a bacterial-caused sickness. The most common cause of mortality among the elderly is bacterial pneumonia. Enhanced sanitation, vaccinations, and medicines have all reduced bacterial infection death rates, while antibiotic-resistant strains have allowed some diseases to resurface. Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Several strains had evolved resistance to one or more of the most commonly used antibiotics.
Examples of Bacterial Infections:
- Bacterial Meningitis
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
- Gastritis and Urinary Tract Infections
- Food Poisoning
Track 5 Vaccines and Immunization
A vaccination is a cellular preparation that gives you the protection you need against a specific infectious illness. A biological preparation of disease-causing bacteria is included in the vaccination. A weakened or destroyed version of the bacterium, one of its surface proteins, and its toxins are seldom used in this preparation. Immunization can be therapeutic (to treat a disease that has already developed, such as cancer) or preventive (to prevent the given disease) (to prevent or ameliorate the effects of a future infection by a natural or wild pathogen).
- Human Vaccines - Infectious Diseases & Non Infectious Diseases
- Cancer and Immunotherapy Vaccines
- HIV Vaccines
- Veterinary Vaccines
- Vaccine Adjuvants
- Pediatric Vaccines
- Plant Based Vaccines
Track 6 Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents
Infectious diseases that afflict children are known as pediatric infectious disorders. An infectious diseases specialist has the skills and training to effectively identify and treat a kid who develops recurrent illness as a result of an infectious agent from infancy through puberty. In and on our bodies, there are numerous microbes. They're usually harmless or even helpful, but under some circumstances, a few living forms might cause illness. Some infectious diseases can be handed on from one person to the next. Some are spread by insects or animals. Others are acquired by the ingestion of contaminated food or drink. The symptoms and side effects vary depending on the organism that caused the infection, however fever and tiredness are common.
- Transplant Infections
- Severe and Complicated Infections
- Tetanus and Polio
- Streptococcal Pharyngitis
- Scarlet Fever
- Campylobacteriosis
Track 7 Controlling Nosocomial Infections
Nosocomial infections are illnesses contracted in a hospital and may be caused by organisms that are resistant to drugs. A nosocomial infection is one that was not present or incubating before to the patient's admission to the hospital, but that developed within 72 hours after admission.
Control: Nosocomial infections can be managed by evaluating and comparing infection rates within a healthcare environment and adhering to optimum healthcare practices. The approach for nosocomial infection surveillance, as well as a study of large outbreaks, is provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Hospital Infection
- Device-Related Infections
- Surgical Site Infections
- Opportunistic Infections
Track 8 Infectious Diseases Caused by Viruses
When pathogenic viruses infiltrate an organism's body, infectious virus particles (virions) adhere to and penetrate vulnerable cells, causing viral illness. Viruses can cause significant, perhaps fatal complications such as dehydration, bacterial pneumonia, and other secondary bacterial infections in some situations. Furthermore, sexually transmitted viral illnesses like HIV/AIDS and HPV can cause major consequences and even death.
Examples of Viral Infections Diseases:
- Respiratory Viral Diseases
- Gastrointestinal Viral Diseases
- Hepatic Viral Diseases
- Cutaneous Viral Diseases
- Hemorrhagic Viral Diseases
- Neurologic Viral Diseases
- Bottom Line Infections
Track 9 Veterinary Diseases
Veterinary medicine may be a discipline of medication that deals with the interference, diagnosis, control, and treatment of unhealthiness, disorder, and harm in animals. It additionally deals with animal rearing, breeding, husbandry, still as nutrition and products development analysis. Medicine covers a good vary of animal species, each domesticated and wild, still as a good vary of sicknesses which will have an effect on varied species.
Examples of veterinary Diseases:
- Zoonosis
- Foot Rot
- Anthrax
- Ephemeral Fever
- Rabies
- Brucellosis
- Foot And Mouth Disease
Track 10 Fungal Infectious Diseases
Infections caused by fungi are quite widespread all over the world. Fungal infections in humans arise when an invasive fungus takes over a region of the body and the immune system is unable to control it. Fungi may be found in soil, plants, water, and the atmosphere. Mycoses are fungal illnesses that affect people and include coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and blast mycosis. These infections can be mild, such as an upper respiratory infection, or they can be severe, affecting the entire body, including the bloodstream and organ systems.
Examples of Fungal Infectious Diseases:
- Yeast Infection
- Ringworm
- Invasive Allergies
- Chronic Lung or Deep Tissue Infections
- Mucosal Infection
Track 11 Tropical Infectious Diseases
Tropical illnesses are those that are only found in or are exclusive to tropical and subtropical areas. In temperate areas, disease propagation is much less due to the advent of a cold season, which reduces the bug population by inducing hibernation. Insects such as mosquitoes and flies are the most prevalent disease carriers or vectors. These insects may contain a bacteria or virus, as well as a parasite, that is harmful to people and animals. Insect "bite" is the most common way for most diseases to spread, and it also spreads the infectious agent through subcutaneous blood exchange. Vaccines for the majority of illnesses are still unavailable.
- Immunizations for TID's
- Diagnosis of Immunizations for TID's
- Neglected Tropical Diseases
- Tropical Medicine and Health
Track 12 STD and HIV Infection
Sexually transmitted illnesses, generally known as STDs, are infections that are communicated by sexual activity, particularly vaginal intercourse, oral sex, and anal sex. Because STIs seldom produce symptoms at first, there is a higher risk of spreading the disease to others. Vaginal discharge, pelvic discomfort, ulcers on or around the genitals, and penile discharge are all symptoms and indicators of STIs. STIs can be transmitted to a newborn before or after childbirth, which can lead to bad results for the kid. Infertility can be caused by certain STIs. Safe sex behaviors including using condoms, having fewer sexual partners, and being in a relationship where each person only has sex with each other reduce the risk of STIs. Adult male circumcision may be beneficial in preventing certain infections.
Examples of STDs Infection:
- Chlamydia
- Trichomoniasis
- Gonorrhea
- HPV
- Syphilis Hepatitis B Infection
Track 13 Neuro Infectious Diseases
Neuro infectious illnesses can damage the nervous system, from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and nerves. Furthermore, the majority of neuro infectious illnesses include encephalitis and meningitis, in which bacterial or viral infection causes inflammation of the membranes protecting the brain and spinal cord, which can result in impairment or death.
It is a medical specialty that promotes scientific study in the areas of neurophysiology, prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment of neurological illnesses caused by bacteria or viruses that impact the nervous system.
Examples of Neuro Infectious Diseases:
- Meningitis and Encephalitis
- Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
- HIV-Associated Neurodegeneration
- HTLV 1 Myelopathy Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis
- Neuro-Infections Induced Autoimmune Disorders
Track 14 Infection, Immunity and Inflammation
Disease can be caused by bacteria or viruses invading the body. Bacteria, viruses, protozoans, and fungus are some of the microorganisms that cause infection.
Immunity refers to the body's defense system against illnesses and infections. The immune response is a biological response that protects your body from invading cells, chemicals, and tissues. The spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, particular deposits of lymphoid tissue (such as those in the gastrointestinal tract and bone marrow), macrophages, lymphocytes (including T cells and B cells), and antibodies are all part of the immune system.
- Molecular Pathogenesis
- Cellular Microbiology
- Virulence Factors
- Host Resistance
Track 15 Pharmacology of Infectious Diseases
The study of a drug's or medication's action is pharmacology, a field of medicine and pharmaceutical sciences. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are the two primary branches of pharmacology. Pharmacodynamics is associated with the study of a drug's impacts on biological systems, while pharmacokinetics is associated with the study of a drug's effects on biological systems. Pharmacokinetics is concerned with the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of chemicals from biological systems, whereas pharmacodynamics is concerned with the interactions of chemicals with biological receptors.
Track 16 Internal Medicine for Infectious Diseases
Internal medicine practitioners, often known as general internal medicine specialists or general medicine physicians in Commonwealth nations, are educated to address complicated or multisystem illness situations that single-organ disease practitioners may not be equipped to handle. They may be requested to deal with undifferentiated presentations that fall beyond of a single-organ specialty's scope of practice, such as dyspnea, exhaustion, weight loss, chest discomfort, disorientation, or a change in consciousness. They can treat significant acute illnesses that impact many organ systems in a single patient at the same time, as well as multiple chronic diseases or "comorbidities" that a single patient may have.
- Adolescent Medicine
- Adult Immunization
- Internal Medicine and Critical Care
- Telemedicine
- Internal Medicine and Clinical trails
Track 17 Clinical and Case Reports
Case reports may provide a patient's demographic data, but they generally describe an exceptional or original event. Case reports have long been an important part of medical education, since they provide a framework for case-based learning and application. A case report is a complete account of a patient's symptoms, diagnosis, signs, therapy, and follow-up in medicine. Only a few additional case reports include a literature evaluation of previously known instances. Case reports are expert narratives that provide input on clinical practice recommendations and provide a framework for early warning signs of adverse events, efficacy, and cost. They can be disseminated for educational, scientific, or medicinal objectives.
Track 18 Blood Infectious Diseases
Blood-borne pathogens such as bacteria, fungus, viruses, and parasites can invade our bloodstream and cause infectious disorders. Bacteria can enter your bloodstream through wounds or through another infection like pneumonia or a urinary tract infection. Viruses including influenza, dengue fever, hepatitis B, poliovirus, and HIV, as well as parasites like plasmodium and trypanosome brucei, can all infiltrate your circulation.
Examples of blood Infectious Diseases:
- Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
- Human Immuno-Deficiency Virus
- Giardiasis
- Infectious Mononucleosis
- Blood Disorders
- Contamination of Blood Products
- Infections affecting White Blood Cells
Track 19 Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of health and disease situations in specified populations, including their distribution (who, when, and where), trends, and factors. Epidemiologists assist with research design, data gathering, statistical analysis, and findings interpretation and dissemination
Major areas of epidemiological study case include:
- Scientific
- Systematic
- Data Based
- Natural Disaster
Track 20 Parasitology & Infectious Diseases
Parasitology is the study of parasites and their hosts, as well as their interactions. In biological terms, the breadth of parasitology is governed by the way they exist rather than the organism or environment. Parasites reduce host fitness by general or specific disease, and they also influence the human body in a variety of ways, including through the oral route, skin, arthropod vectors, and sexual interaction. Several laboratory techniques, such as imaging techniques and endoscopy, are used to diagnose parasite infections.
Types of parasitology:
- Veterinary Parasitology
- Structural Parasitology
- Quantitative Parasitology
- Molecular Parasitology
- Medical Parasitology
Track 21 Plants Diseases and Infection Control
Plant disease is a change in a plant's normal state that affects or stops its important functioning. Depending on the causal agent, plant diseases can be classed as noninfectious or infectious. Plant diseases cost farmers a lot of money all around the world. Plant disease control is critical for reliable food production, and it causes considerable issues in agricultural land, water, fuel, and other input consumption. Plants have inherent disease resistance in both natural and cultivated populations, but there are numerous examples of devastating plant disease impacts, such as the Great Famine of Ireland and chestnut blight, as well as recurrent severe plant diseases like rice blast, soybean cyst nematode, and citrus canker.
Examples of Plant Diseases:
- Leaf rust (common leaf rust in corn)
- Stem rust (wheat stem rust)
- Sclerotinia (white mold)
- Powdery mildew
Track 22 Antimicrobials/Antibiotics/Antibacterial
An antimicrobial drug is an agent that either stops the growth of microorganisms or kills them. Antimicrobial medicines can be assembled by how they act basically against the organism. For example, antifungals are used against fungi, and antibiotics are used against bacteria. Classification of them can be made according to their function. Agents that merely inhibit their growth are called bacteriostatic agents, while agents that kill microbes are microbicides. The use of antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis, while the use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy.
- Spectrum of Activity
- Effect on Pathogen
- Mode of Action
Track 23 Sepsis/Septicemia
Septicemia, also known as Sepsis, is a potentially fatal complication that occurs when germs from another infection enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. It requires immediate medical care since it can cause organ failure, tissue damage, and death. Sepsis is an extremely serious condition that arises when an infection goes awry. The immune system is suppressed beyond this early stage. Fever, increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, and disorientation are all common indications and symptoms. Symptoms of a particular illness, such as a cough with pneumonia or painful urination with a kidney infection, may also be present. The extremely young, the elderly, and those with a compromised immune system may show no signs or symptoms of an illness, and their body temperature may be low or normal rather than high. Severe sepsis impairs organ function as well as blood flow. Limited blood pressure, high blood lactate, and low urine output can all indicate inadequate blood flow. Low blood pressure caused by sepsis that does not improve after fluid replacement is referred to as septic shock.
Track 24 Ebola and Zika Viral Infections
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) or Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever caused by Ebola viruses in humans and other animals. Fever, pharyngitis, muscle soreness, and headaches are common signs and symptoms that appear two to three weeks after catching the virus. Vomiting, diarrhea, and a rash are common side effects, as is liver and renal dysfunction.
Zika Viral Infection:
Zika virus illness, often known as Zika fever, is an infectious disease caused by the Zika virus. The majority of cases have no symptoms, but when they do appear, they are generally mild and might be mistaken for dengue fever. A increase in fever, red eyes, joint discomfort, and a headache are all possible symptoms.
Track 25 Orthopedic Infections
Orthopedic surgery is a type of surgery that deals with problems with the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine problems, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, cancers, and congenital abnormalities with both surgical and nonsurgical methods. These infections can arise on their own, but they are more commonly a consequence of surgery, particularly joint replacement operations.
Adult Trauma Orthopedics: Orthopedic trauma is a wide term that refers to a variety of injuries ranging from minor fractures to life-threatening incidents.
- Orthopedic Infections
- Pediatric Orthopedics
- Adult Trauma Orthopedics
- Advanced Clinical Clerkship In Orthopedic Oncology
Track 26 Non communicable Diseases
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), often known as chronic illnesses, are diseases that cannot be communicated from one person to another. Cardiovascular illnesses, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases are the four primary classifications, and they impose a significant and rising burden on health and development.
Examples of Non communicable Diseases:
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Cancer
- Epilepsy
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Cerebrovascular Disease (Stroke)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Coronary Artery Disease.
Track 27 Problems in Infectious Disease Practice
Infection control in a health care institution refers to the prevention of germs from spreading from one person to another. Frequent hand washing, infection outbreak management, hygienic water, and food in the hospital must all be maintained to prevent these infectious disorders.
Errors in Diagnosis: At any of these points, diagnostic mistakes can arise. Diagnostic mistakes occur when a doctor fails to offer a correct and timely explanation of a patient's health concerns, or when that explanation is not communicated to the patient.
Treatment Failure: A measure of the quality of health care based on the evaluation of failed outcomes of illness management and treatments in individual instances or series.
- Diagnostic Errors
- Treatment Failure
Track 28 Viruses and Cancer
Cancer is a condition that is characterized by uncontrolled cell growth that can invade and spread to other regions of the body. A lump, odd hemorrhage, a chronic cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel processes are all signs and symptoms to look out for. Around 100 distinct varieties of cancer impact humans. The human papillomavirus is the most common virus connected to human malignancies. While papillomaviruses are not malignant in and of themselves, they are linked to an increased risk of cancer.
Types of cancers:
- Non-melanoma Skin Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Colon and Rectal Cancers
- Melanoma
- Bladder Cancer
- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Track 29 Critical Care and its Applications
By obtaining, debating, disseminating, and promoting evidence-based material important to intensivists, Critical Care aspires to enhance the care of critically sick patients. Critical care is reserved for hospital patients with life-threatening illnesses who require constant medical attention and monitoring. Patients in intensive care units, often known as ICUs, are looked after by a team of professionals that includes: Specially trained nurses, Physicians. Critical care nursing is a branch of nursing that focuses on providing the best possible care to critically sick or unstable patients who have experienced major damage, surgery, or are suffering from life-threatening illnesses.
Critical care Applications:
- Aspects of the patient's condition that necessitate a thorough examination
- Medication with a high-intensity effect
- Ongoing treatment and interventions
- Encouraging commitment to medical ethics principles
- Providing comprehensive care to patients and their families
Infectious Diseases Therapeutic Market
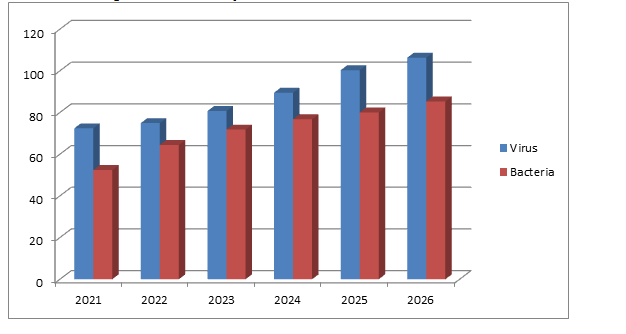
The Middle East and Africa Infectious Disease Therapeutics Market accounts for $72.4 billion in 2021 to $106.3 billion by 2026, at compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.0% for the period of 2021-2026.The Middle East and Africa Infectious disease therapeutics market are categorized based on Mode of treatment into Drugs and Vaccines. The drugs are further segmented into oral administration, topical, injections and others. Based on the target organism the market is categorized into antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiparasitic and others. Based on infection type the market is categorized into Bacterial, viral, fungal, parasite and others. Based on distribution channels the market is categorized into hospitals, clinics and others. Based on Geography, the Middle East and Africa Infectious disease therapeutics market is analyzed under various regions namely the Middle East and Africa
Infectious Diseases Conf 2022 is nonpareil and open platform to explore and gain the knowledge in the field of Life science. This conference brings together professors, researchers, scientists, students in all the areas of medical sciences, pharmaceutical, Life sciences, Medical associations and societies, enables an international forum to explore the approved research. ConferenceSeries Ltd is delight to invite you all to attend and register for the “17th World Conference on Infectious Diseases, Prevention and Control ” scheduled for April 25-26, 2022 at Amsterdam, Netherlands.
The organizing committee is gearing up for an exciting and informative conference program this year also which includes plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at the Infectious Diseases Conf 2022, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world. All members of the Infectious Diseases Conf 2022 organizing committee look forward to meeting you in Barcelona, Spain.
For more details please visit: https://infectious-diseases.conferenceseries.com/
Conference Highlights:
- Infectious Diseases Prevention and Control
- Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19)
- Medical and Vaccine Research for Covid-19
- Infectious Diseases Caused by Bacteria
- Vaccines and Immunization
- Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents
- Nosocomial Infections
- Infectious Diseases Caused by Viruses
- Veterinary Diseases
- Fungal Infectious Diseases
- Tropical Infectious Diseases
- STD and HIV Infection
- Neuro Infectious Diseases
- Infection, Immunity and Inflammation
- Pharmacology of Infectious Diseases
- Internal Medicine for Infectious Diseases
- Blood Infectious Diseases
- Clinical and Case Reports
- Epidemiology
- Infectious Diseases Prevention, Control and Cure
- Plants Diseases and Fungal Infection Control
- Antimicrobials/Antibiotics/Antibacterial
- Sepsis/Septicemia
- Ebola and Zika Viral Infections
- Orthopedic Infections
- Non communicable Diseases
- Problems in Infectious Disease Practice
- Viruses and Cancer
- Critical Care and its Applications
List of Infectious Diseases Hospitals in Amsterdam
- VU University Medical Center VU medisch centrum (VUMC), Amsterdam
- Academic Medical Center Academisch Medisch Centrum (AMC), Amsterdam
- University Medical Center Groningen Universitair Medisch Centrum Groningen (UMCG), Groningen
- University Medical Center Utrecht Universitair Medisch Centrum Utrecht (UMCU), Utrecht
- Leiden University Medical Center Leids Universitair Medisch Centrum (LUMC), Leiden
- Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Radboudumc (also: UMC Nijmegen, Universitair Medisch Centrum St. Radboud), Nijmegen
- Maastricht UMC+ Maastricht Universitair Medisch Centrum (MUMC+), Maastricht
- Erasmus MC Erasmus MC, Rotterdam
List of Infectious Diseases Hospitals around the World:
- Artemis Hospitals
- Manipal Goa Hospital
- BLK Super Speciality Hospital
- Centro Médico Teknon
- Anadolu Medical Center
- Kucukcekmece Hospital
- Sourasky Medical Center
- Helios Berlin Buch
List of Infectious Diseases Universities in Amsterdam
- Utrecht University
- University of Amsterdam
- Erasmus University Rotterdam
- University of Groningen
- Radboud University Nijmegen
List of Infectious Diseases Companies in Amsterdam
- Agendia
- Avantium
- Caelus Health
- Corbion
- Lava Therapeutics
- Leyden Labs
- LUMICKS
- Meatable
- NorthSea Therapeutics
- Oncosence
Universities Related to Infectious Diseases
- University of Cardenal Herrera, Spain
- University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain
- University Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla, Spain
- University of Maryland Medical Center, Spain
- University of Liverpool-Institute of Infection and Global Health, Spain.
- Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
- University of Barcelona, Spain
- University of Oxford, United Kingdom
- Generalitat de Catalunya, Spain
- University of Malaga, Spain
- University of Cukurova, Turkey
- Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany
- University of British Columbia, Canada
- Texas A&M University- Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, USA
- Brown University-Spain
- National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani, Italy
- San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Italy
- University of the Balearic Islands, Spain
- University of Cantabria, Spain
- University of Cadiz, Spain
- University of Jaen, Spain
- Pompeu Fabra University, Spain
Related Societies and Associations:
Europe: Spanish Society of Paediatric Infectious Diseases, Spain; Spanish Society of Paediatric Clinical immunology and Allergy, Spain; Spanish Association of Paediatric Primary Care, Spain, British Society for Immunology, U.K; European Society for Immunodeficiencies, Switzerland; European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Switzerland; British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, UK; Society for General Microbiology, UK
USA: Infectious Disease Association of California, USA; Infectious Diseases Society of America, USA, The Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, Inc, USA.
Asia Pacific: Infectious Diseases Association of Thailand, Thailand; Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society for Thailand, Thailand; The Swiss Society for Infectious Diseases, Switzerland, Society of Infectious Disease, Singapore, New South Wales Infection Control Association, Australia.
Middle East: Infectious diseases and microbiology association – Bahrain; Cyprus Society of Chemotherapy and Infectious Diseases; Egyptian African Society of Microbiology & Infectious Diseases; The organization of hospital infection control in Turkey; Emirates Society of Clinical Microbiology-ESCM; Health crisis in Yemen
Conference Highlights
- Infectious Diseases Prevention, Control and Cure
- Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19)
- Medical and Vaccine Research for Covid-19
- Infectious Diseases Caused by Bacteria
- Vaccines and Immunization
- Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents
- Controlling Nosocomial Infections
- Infectious Diseases Caused by Viruses
- Veterinary Diseases
- Fungal Infectious Diseases
- Tropical Infectious Diseases
- STD and HIV Infection
- Neuro Infectious Diseases
- Infection, Immunity and Inflammation
- Pharmacology of Infectious Diseases
- Internal Medicine for Infectious Diseases
- Clinical and Case Reports
- Blood Infectious Diseases
- Epidemiology
- Parasitology & Infectious Diseases
- Plants Diseases and Infection Control
- Antimicrobials/Antibiotics/Antibacterial
- Sepsis/Septicemia
- Ebola and Zika Viral Infections
- Orthopedic Infections
- Non communicable Diseases
- Problems in Infectious Disease Practice
- Viruses and Cancer
- Critical Care and its Applications
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | September 28-29, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
- Air & Water Borne Diseases
- Journal of Bacteriology & Parasitology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by